SQL Restore: restoring SQL databases with the SQL Restore Utility
BackupAssist provides an inbuilt SQL Restore Utility that can be used to restore SQL databases to both local and remote SQL Servers1. In addition, you can restore databases to a specific point in time provided that you have a transaction log backup of the database.
While you do need to have BackupAssist installed to use the restore utility, it does not have to be a licensed installation of the software. In addition, if the trial expires you can still access the utility by running SQLRestore.exe from the BackupAssist installation directory.
Accessing the SQL Restore Utility
- Click
 Restore in the navigation bar.
Restore in the navigation bar. - Click
SQL restore.
- Alternatively, run SQLRestore.exe from the directory where BackupAssist was installed.
- The SQL Restore Utility will launch and attempt to detect for both local and remote SQL servers that can be restored to.
- Local server: select the local server you wish to restore to from the list of detected servers.
- Note: If the SQL server you wish to restore to is not running or 'stopped', click Attempt to start. Any servers that cannot be started may indicate a fault with the server itself. You can only restore to SQL servers that are running. Consult your system administrator if any SQL servers will not start.
- Remote server: select the Restore a remote server radio button and choose a server from the drop-down list.
- Note: if the remote server you want to restore to is not in the list or no remote servers were detected you can type the server's name or IP address directly into the field.
- Click next and BackupAssist
will attempt to connect to the SQL server using the BackupAssist user identity credentials.
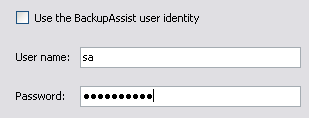
- Note: if BackupAssist is unable to authenticate to the server you will be asked to input a valid username and password. If the SQL server you are restoring to only accepts SQL authentication or requires a different Windows user uncheck Use the BackupAssist user identity and input a valid username and password.
- Note: if BackupAssist is unable to authenticate to the server you will be asked to input a valid username and password. If the SQL server you are restoring to only accepts SQL authentication or requires a different Windows user uncheck Use the BackupAssist user identity and input a valid username and password.
- Select a restore type.
- Note: multiple restore types can be selected. The master database is restored first before selected databases.
Master database recovery (local SQL server only)
Use this option to restore the master database to a local SQL server. The master database is composed of system tables and catalogs that store information about other databases, login accounts, configuration and security settings, and so on. The master database is critical to your SQL server so it is essential that you have a current backup to restore from. In addition, if you are restoring your SQL server after a disaster or new installation, it is advised that you restore the master database before restoring any other database; doing so eliminates the hassle of having to manually recreate each database individually as well as ensuring that all security information is preserved. Master database recovery will not be available if you are restoring to a remote SQL server.
Instructions on master database recovery
Selected databases restore
Use this option to restore one or more databases to either a local or remote SQL server. The databases you wish to restore must already exist on the SQL server. You can either choose to use the SQL Restore Utility to restore the master database first, which will result in recreating all databases on the server, or you can manually recreate each database you wish to restore.
Instructions on selected databases restore